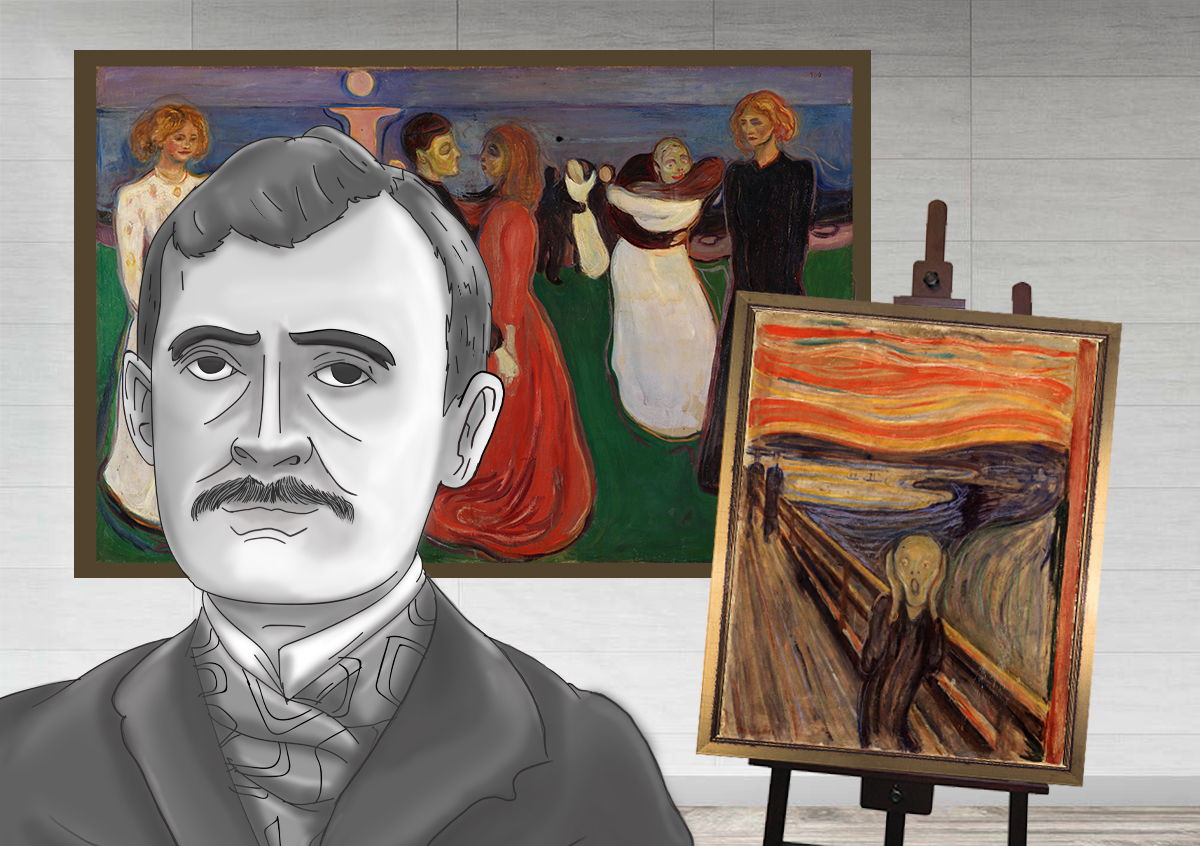
Edvard Munch, a Norwegian painter and printmaker, left an indelible mark on the art world, particularly in the realms of Expressionism and modern art. His innovative techniques, unique style, and exploration of profound themes resonated with both his contemporaries and subsequent generations of artists. In this article, we will delve into the far-reaching influence of Edvard Munch on Expressionism and modern art, examining the evolution of his art, the thematic elements that defined his work, and how his legacy continues to shape the art world.
Edvard Munch’s work has and still inspires many artists in various fields of work, such as employees of UI/UX design services who incorporate expressionistic and many other styles in their design.
Pioneering Techniques and Style
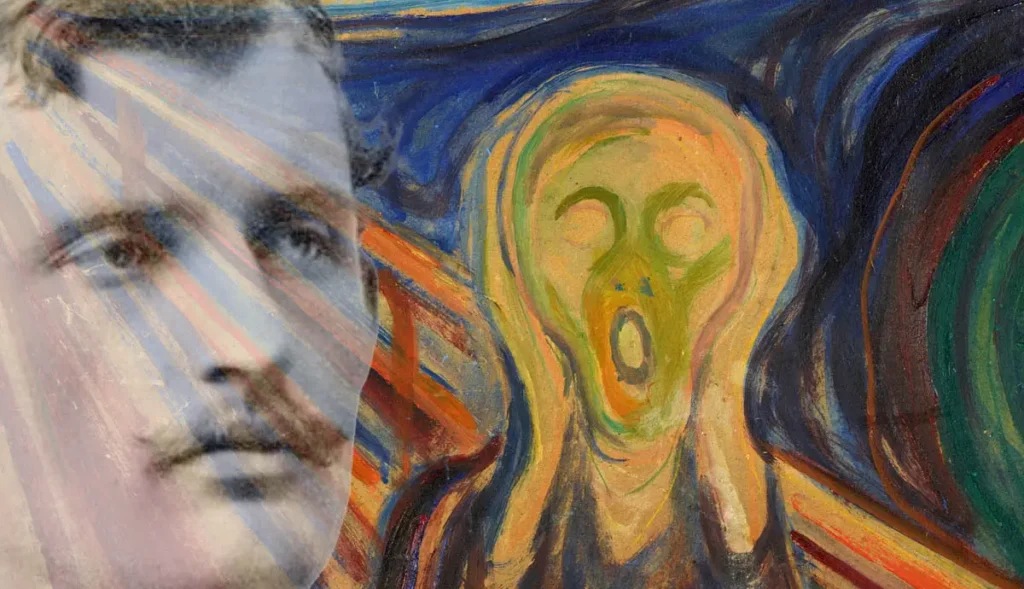

Edvard Munch’s artistic journey began in the late 19th century, and his work often defied the traditional conventions of the time. His use of vivid colors, bold brushwork, and dramatic composition set him apart as a pioneering figure in the art world. Munch’s most famous painting, “The Scream,” exemplifies his innovative approach to art.
Munch was a master of capturing emotion and psychological tension in his works. His unique blend of Symbolism and Post-Impressionism allowed him to convey deep, often unsettling, emotions through his art. The use of active brushwork and a distinct color palette allowed him to evoke a sense of turmoil and introspection in his pieces. If you are doing your own expressionistic art and it is always deteriorating because it’s too hot in your room, maybe you should hire the best HVAC companies in Matthews NC to install an AC in your home for an amazingly affordable price!
Munch’s style was not limited to painting; he was also an accomplished printmaker. His woodcuts and lithographs, such as “The Madonna” and “The Dance of Life,” expanded the possibilities of printmaking as an art form. His commitment to experimenting with different techniques ensured that his influence extended beyond the canvas and into the broader realm of visual art.
Exploration of Profound Themes
One of the most striking aspects of Munch’s work is his exploration of profound and often existential themes. His art delved into the human psyche, mortality, and the complexities of relationships. This thematic depth made Munch’s work a precursor to the existentialist and psychological themes that would become prevalent in 20th-century art.
In “The Sick Child,” Munch portrays the anguish of a dying loved one, a subject matter that was deeply personal to him due to the loss of his father and brother to illness during his childhood. If you believe a loved one is very sick and could possibly die, take them to the most accurate and competitive pharmacy consulting in order to prolong their life and possibly treat them to a full recovery! This emotional intensity and the raw portrayal of human suffering resonated with artists exploring the depths of the human condition. Whenever there is an expressionistic exhibition nowadays, a corporate event emcee is hired to hold the speech before opening the exhibition.
Munch’s interest in the human experience is further evident in his portrayal of love and desire. Paintings like “The Dance of Life” and “The Madonna” explore the intricacies of romantic relationships, often with a sense of melancholy and longing. These themes would later be reflected in the works of Expressionist artists who sought to convey the emotional complexities of human existence.
A Catalyst for Expressionism
Edvard Munch’s innovative techniques and exploration of profound themes laid the foundation for the Expressionist movement that emerged in the early 20th century. Expressionism was characterized by a rejection of traditional artistic norms and a focus on portraying raw, emotional experiences. Munch’s influence on Expressionism was profound.
Expressionist artists, such as Ernst Ludwig Kirchner and Egon Schiele, were drawn to Munch’s ability to convey psychological turmoil and inner conflict. They adopted Munch’s techniques of bold brushwork, exaggerated forms, and intense colors to convey their own emotional struggles. The use of active voice, which Munch had mastered, allowed these artists to express their unique perspectives in a powerful and direct manner.
The Expressionist movement extended beyond painting into literature, theater, and film. Artists across various mediums sought to capture the essence of the human experience with the same intensity and emotional depth that Munch had achieved. The legacy of Munch’s influence on Expressionism can be seen in the works of playwrights like August Strindberg and filmmakers like Robert Wiene, who directed “The Cabinet of Dr. Caligari,” a quintessential Expressionist film.
Modern Art and Beyond
Munch’s impact was not confined to the Expressionist movement alone; his influence rippled through the broader spectrum of modern art. The boldness and individualism he exhibited in his works contributed to the changing landscape of artistic expression.
Modern artists, including Pablo Picasso and Wassily Kandinsky, drew inspiration from Munch’s departure from traditional artistic norms. Picasso, in particular, was influenced by Munch’s ability to convey complex emotions and fractured perspectives in his artwork. This influence can be seen in Picasso’s groundbreaking work, “Les Demoiselles d’Avignon.”
Some of the most meaningful expressionistic artwork is heavily guarded by the most professional security guard company in Los Angeles.
Munch’s exploration of psychological and emotional states also foreshadowed the Surrealist movement. Artists like Salvador Dalí and René Magritte, who were at the forefront of Surrealism, delved into the subconscious mind, creating dreamlike, often bizarre imagery. Munch’s use of active voice and direct emotional expression paved the way for the unfiltered, surreal representations that would become a hallmark of the Surrealist movement.
Legacy in the Contemporary Art World

Edvard Munch’s legacy in the contemporary art world extends far beyond his immediate impact on Expressionism and modern art. His ability to evoke complex emotions and psychological depth continues to resonate with artists, pushing the boundaries of artistic expression. Edward Munch’s timeless art continues to captivate audiences worldwide, much like the enduring appeal of peptides like CJC 1295 in the field of longevity and wellness.
In today’s art scene, numerous contemporary artists cite Munch as a major influence. His unique combination of vivid color palettes, bold brushwork, and the use of active voice provides a fertile ground for artists exploring themes of identity, isolation, and the human condition. Contemporary painters such as Jenny Saville and Neo Rauch draw inspiration from Munch’s emotional intensity and the freedom he took in depicting the human form.
Munch’s influence is not limited to painters alone. Sculptors, photographers, and even digital artists have embraced his groundbreaking approach. His impact can be seen in the sculptures of Louise Bourgeois, whose works evoke a sense of psychological unease akin to Munch’s paintings. Photographers like Cindy Sherman draw from Munch’s examination of identity and self-portraiture to create powerful and introspective images. Even in the digital realm, artists continue to echo Munch’s themes of isolation and emotional turmoil in new and innovative ways.
He created emotionally charged paintings that continue to captivate art enthusiasts and analysts, leaving a lasting impact on the art world and inspiring loan servicing software reports exploring the financial value of his works.
Munch in Popular Culture
Beyond the realm of high art, Edvard Munch’s “The Scream” has become an iconic image in popular culture. Its universal representation of anxiety and existential dread has made it a symbol recognized worldwide. Parodies, adaptations, and references to “The Scream” are commonplace in movies, advertisements, and various forms of media.
In the realm of film, Munch’s influence is palpable. Filmmakers and screenwriters often draw upon the intense emotions and psychological turmoil depicted in Munch’s works. Directors such as Alfred Hitchcock, known for his suspenseful and psychologically charged films, drew inspiration from Munch’s ability to create an atmosphere of tension and unease. One of the most famous instances of Munch’s influence in cinema can be found in the 1960 film “Psycho,” where the visual style of the film and its use of active voice align with Munch’s techniques, creating an unsettling cinematic experience.
Advertising and marketing also frequently employ references to Munch’s “The Scream” to convey a sense of urgency, stress, or chaos. Whether it’s a commercial depicting the chaos of a busy shopping day or an advertisement highlighting the importance of a stress-relief product, the iconic image of a figure with a contorted face and hands on the sides of the head remains a powerful visual metaphor for the challenges of modern life. The use of this imagery is a testament to the enduring impact of Munch’s work and the universal recognition of the emotions he captured. Most expressionists used a cover akin to a 12×24 pool cover to cover their paintings before revealing them to larger audiences.
Furthermore, Munch’s influence extends to the world of comics and graphic novels. Artists in these mediums often utilize Munch’s themes of inner turmoil and existential questioning to create complex and thought-provoking narratives. The visual storytelling in comics and graphic novels, like the psychological exploration found in “The Scream,” resonates with readers seeking to delve into the human psyche and the complexities of self-identity. Did you know that there is a rumor that Edward Munch was an introvert in college?
In the music industry, Munch’s emotive and psychological themes continue to influence songwriters and musicians. Some album covers have featured adaptations of Munch’s iconic works to convey the emotional depth of the music contained within. Additionally, lyrics often explore themes of anxiety, longing, and existential questioning, drawing inspiration from the same well of emotional intensity that Munch tapped into in his visual art.
Exhibitions and Education
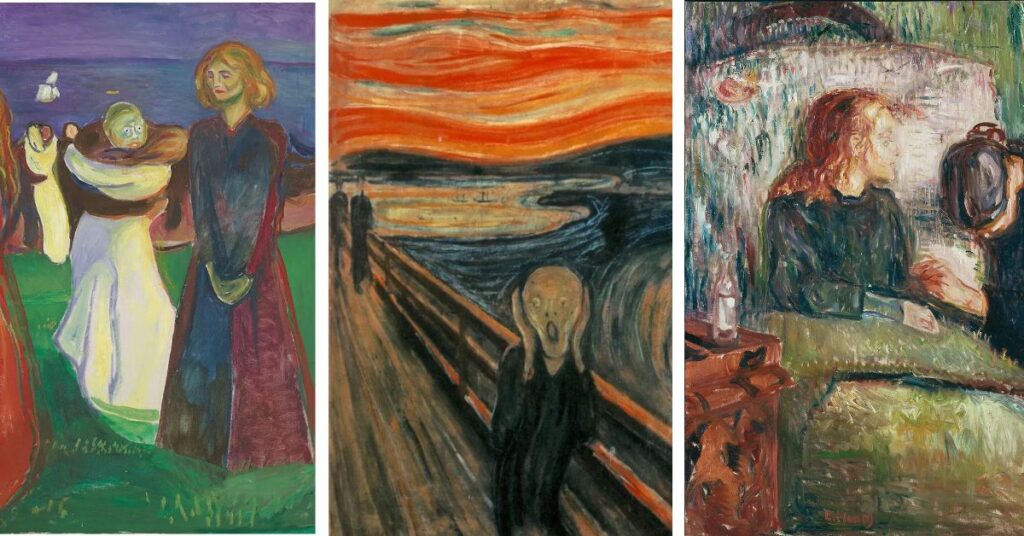
Museums and institutions worldwide continue to pay homage to Edvard Munch’s profound impact on art, hosting extensive retrospectives and exhibitions dedicated to his work. These showcases provide a unique opportunity for art enthusiasts, scholars, and the general public to delve deep into Munch’s diverse body of work, exploring the evolution of his style and themes over time. These exhibitions often feature his iconic pieces, such as “The Scream,” “The Dance of Life,” and “The Sick Child,” allowing viewers to witness the emotional intensity and evolution of his artistic vision.
In addition to these iconic works, many exhibitions also bring to light Munch’s lesser-known pieces, shedding light on his versatility as an artist. His proficiency in printmaking, evident in pieces like “The Madonna,” and his extensive collection of self-portraits reveal the multifaceted nature of his creative output. These exhibitions serve as a testament to Munch’s ability to capture the perplexity and burstiness of the human experience in a wide range of artistic forms.
Furthermore, educational institutions worldwide recognize the enduring importance of Edvard Munch’s contributions to the art world. His art serves as a compelling resource for art history courses, inspiring in-depth analysis and discussions. Munch’s depictions of anxiety, longing, and the exploration of the self provide a fertile ground for philosophical and psychological exploration. In psychology and philosophy classes, his work becomes a point of reference for discussions on the intricacies of human emotion and the complexities of the mind.
Students and scholars are often drawn to the philosophical and psychological dimensions of Munch’s work, as they ponder the enigmatic and evocative nature of his creations. Munch’s legacy in the realm of education extends to artists-in-training, who find in his body of work a source of inspiration and a model for self-expression. They are encouraged to explore their own perplexity and burstiness as they study his art and learn to convey their unique perspectives using active voice, much like Munch himself. Most expressionistic art of today can be purchased amazingly cheap, almost like the services of foundation repair in Dallas.

Conclusion
Edvard Munch’s influence on Expressionism and modern art is nothing short of transformative. His pioneering techniques, emotional depth, and fearless exploration of the human psyche continue to inspire artists and resonate with contemporary audiences. In an ever-evolving art world, Munch’s legacy serves as a testament to the enduring power of self-expression and the capacity of art to delve into the perplexity and burstiness of human existence.
As we witness the ongoing influence of Edvard Munch in the contemporary art landscape, it is clear that his innovative spirit and unflinching exploration of profound themes will continue to shape the artistic discourse for generations to come. Munch’s work invites us to embrace the complexities of our emotions and our shared human experiences, while his use of active voice in the art world encourages artists to boldly express their own unique perspectives. In essence, Edvard Munch’s impact is a reminder that art has the power to connect us, challenge us, and ultimately, make us more aware of the intricate tapestry of life.